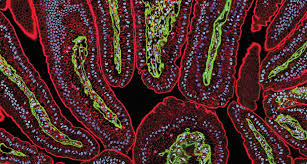
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanoparticles that exhibit unique optical properties due to their small size. They are typically made of materials such as cadmium selenide, cadmium sulfide, or indium arsenide.
Unique Properties of Quantum Dots
- Tunable Emission: The color of light emitted by a quantum dot can be tuned by adjusting its size. Smaller quantum dots emit blue light, while larger ones emit red light.
- High Brightness: Quantum dots are highly efficient emitters of light, producing bright and intense colors.
- Narrow Emission Spectrum: Quantum dots have a narrow emission spectrum, resulting in pure and saturated colors.
- Photostability: Quantum dots are highly resistant to photobleaching, making them ideal for applications that require long-term exposure to light.
Applications of Quantum Dots
- Display Technology: Quantum dots are being used in displays for televisions, smartphones, and other devices to improve color gamut, brightness, and energy efficiency.
- Biomedical Imaging: Quantum dots can be used as fluorescent probes for imaging cells and tissues, enabling early detection of diseases.
- Solar Cells: Quantum dots can be used to improve the efficiency of solar cells by absorbing a wider range of sunlight.
- Lasers: Quantum dots can be used to create lasers with unique properties, such as tunable wavelength and high power output.
- LED Lighting: Quantum dots can be used in LEDs to improve efficiency and color rendering.
Challenges and Future Directions
While quantum dots offer many advantages, there are also challenges to overcome:
- Toxicity: Some quantum dots, particularly those containing cadmium, can be toxic if released into the environment.
- Manufacturing Costs: The production of quantum dots can be expensive, limiting their widespread use in certain applications.
- Stability: Ensuring the long-term stability of quantum dots is a challenge, especially in harsh environments.
Despite these challenges, quantum dots have the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries. As research and development continue, we can expect to see even more innovative applications for these tiny particles in the future.