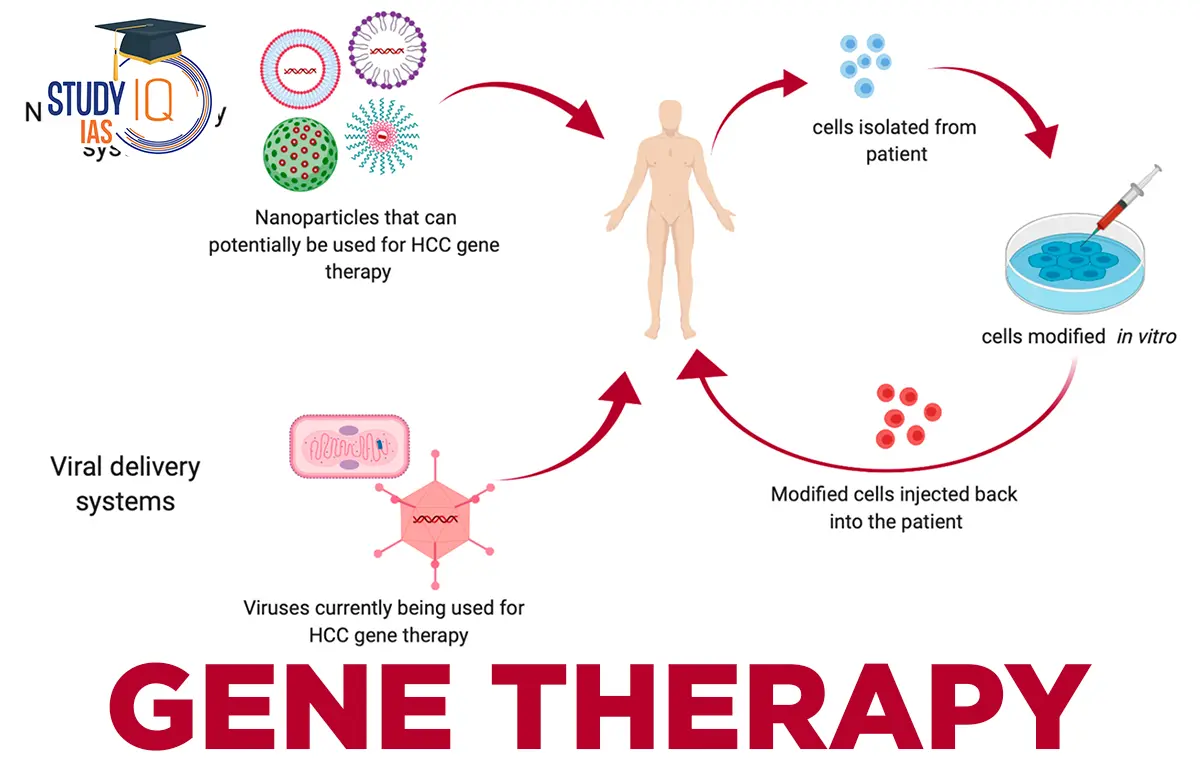
Gene therapy is an innovative approach to treating genetic disorders and diseases by directly modifying a patient’s genes. This cutting-edge technique aims to correct or replace faulty genes responsible for causing illness, offering the potential for long-lasting and, in some cases, curative treatments.
Understanding Gene Therapy
Gene therapy involves several strategies, including:
- Gene Replacement: In this approach, a functional copy of a gene is introduced into a patient’s cells to replace a defective or missing gene. This method is often used for inherited disorders caused by a single gene mutation.
- Gene Editing: Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 allow for precise alterations of the DNA sequence in a patient’s genes. Researchers can delete, insert, or modify specific genes to correct mutations and restore normal function.
- Gene Silencing: This strategy involves inhibiting the expression of a malfunctioning gene, effectively “turning off” the harmful gene product. This method is particularly useful for conditions caused by overactive genes.
- Viral Vectors: Gene therapy often utilizes modified viruses to deliver therapeutic genes into patients’ cells. These vectors can efficiently introduce the desired genetic material while minimizing the risk of triggering an immune response.
Applications of Gene Therapy
Gene therapy has shown promise in various areas of medicine, including:
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions such as cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and hemophilia are being targeted by gene therapy approaches. Early clinical trials have demonstrated success in treating these inherited diseases by restoring normal gene function.
- Cancer Treatment: Gene therapy is being explored as a way to enhance cancer treatments. Strategies include modifying immune cells to better target and destroy cancer cells or introducing genes that inhibit tumor growth.
- Rare Diseases: Many rare genetic disorders lack effective treatments. Gene therapy holds the potential to address these conditions by providing targeted, personalized solutions for patients.
- Infectious Diseases: Researchers are investigating gene therapy as a method to combat viral infections. For example, gene-editing technologies like CRISPR are being tested to target and eliminate the genetic material of viruses such as HIV.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the exciting potential of gene therapy, several challenges remain:
- Safety Concerns: The risk of unintended genetic changes or immune reactions to the therapy can pose significant challenges. Ensuring the long-term safety of gene therapy is crucial for its widespread adoption.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gene therapies must undergo rigorous testing and regulatory approval processes, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Cost and Accessibility: Current gene therapies can be prohibitively expensive, raising concerns about equitable access for all patients in need.
Future Directions
As research continues to advance, the future of gene therapy looks promising. Innovations in gene-editing technologies, such as CRISPR, are likely to drive new discoveries and enhance the precision of gene therapies. Collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies will be vital to overcoming challenges and ensuring the safe and effective implementation of gene therapy in clinical practice.
Conclusion
Gene therapy represents a groundbreaking shift in how we approach the treatment of genetic disorders and diseases. By harnessing the power of genetic modification, this innovative field holds the potential to transform the landscape of medicine, offering hope for patients with previously untreatable conditions. As science continues to unravel the complexities of the human genome, gene therapy may pave the way for a new era of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the unique genetic makeup of each individual.